1
/
of
13
Indigo Ag, Inc.
Carbon Credits - CAR1459
Carbon Credits - CAR1459
Regular price
$50.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$50.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Taxes included.
Couldn't load pickup availability
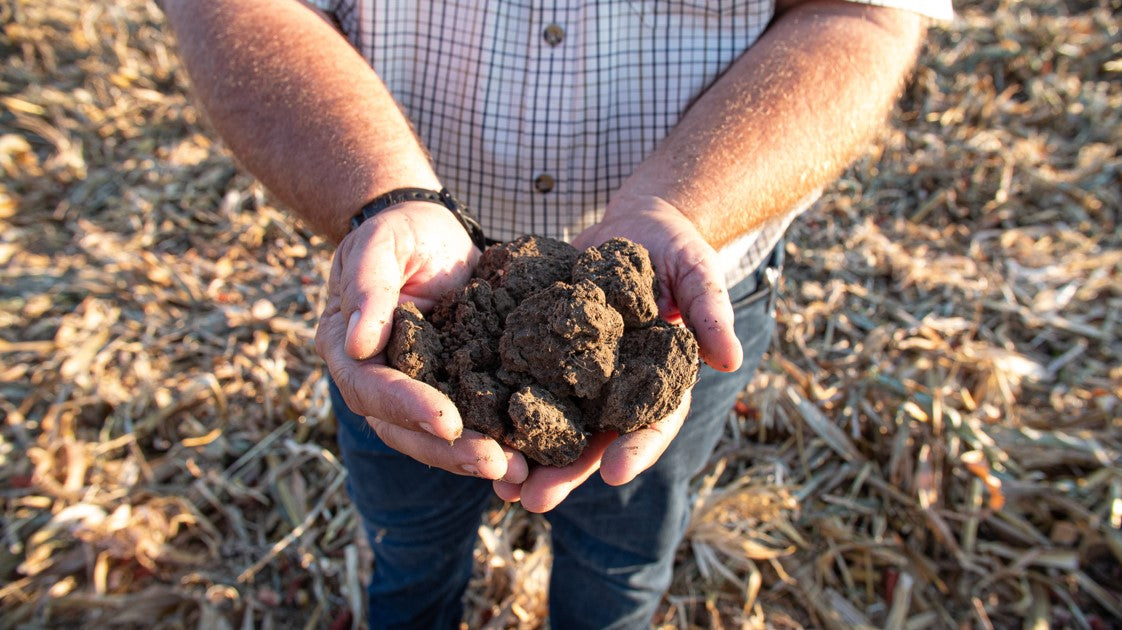
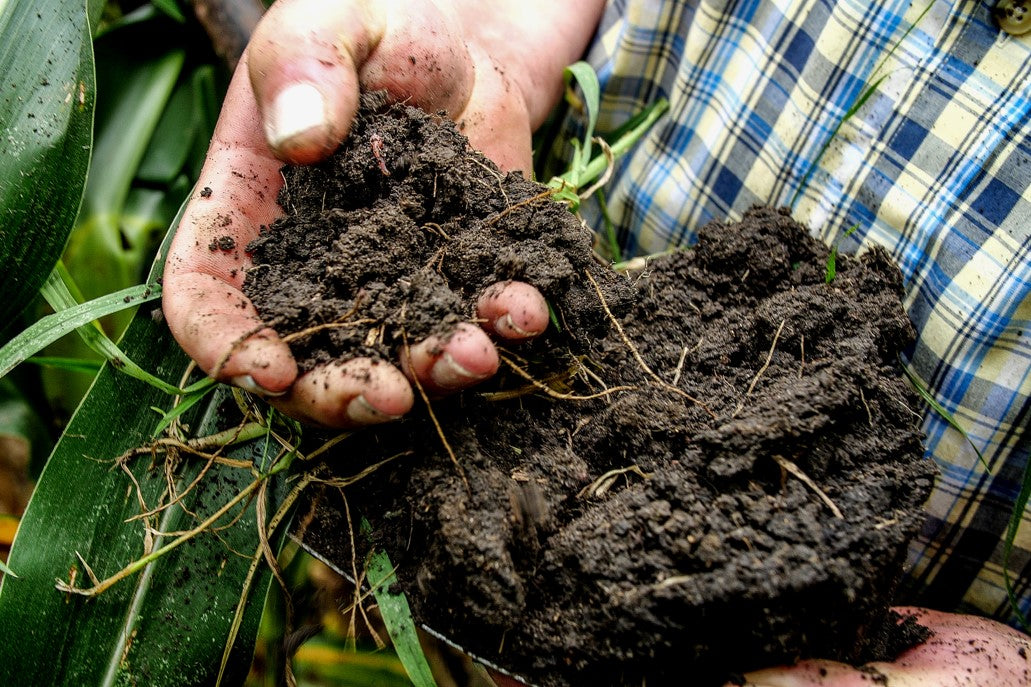
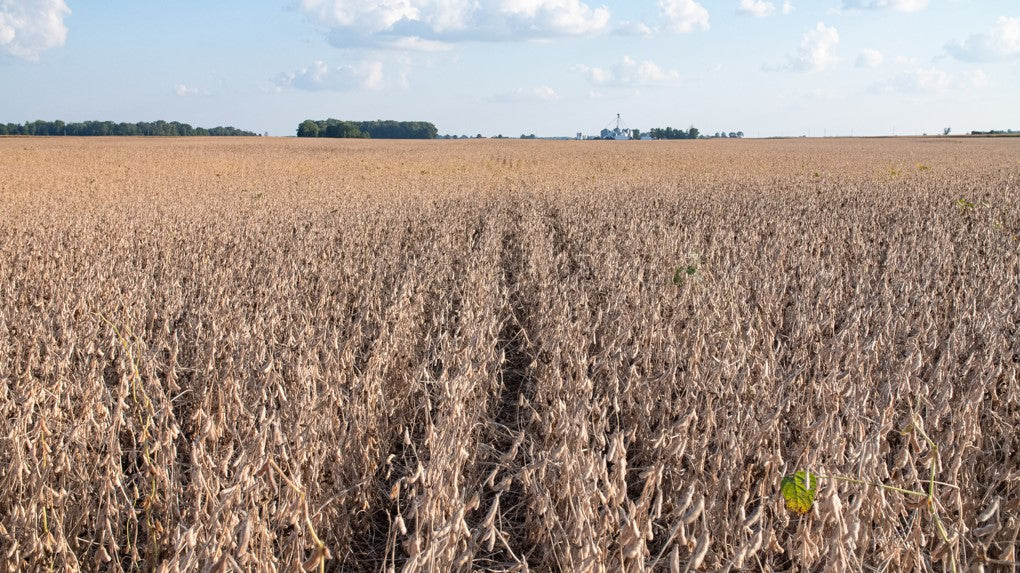
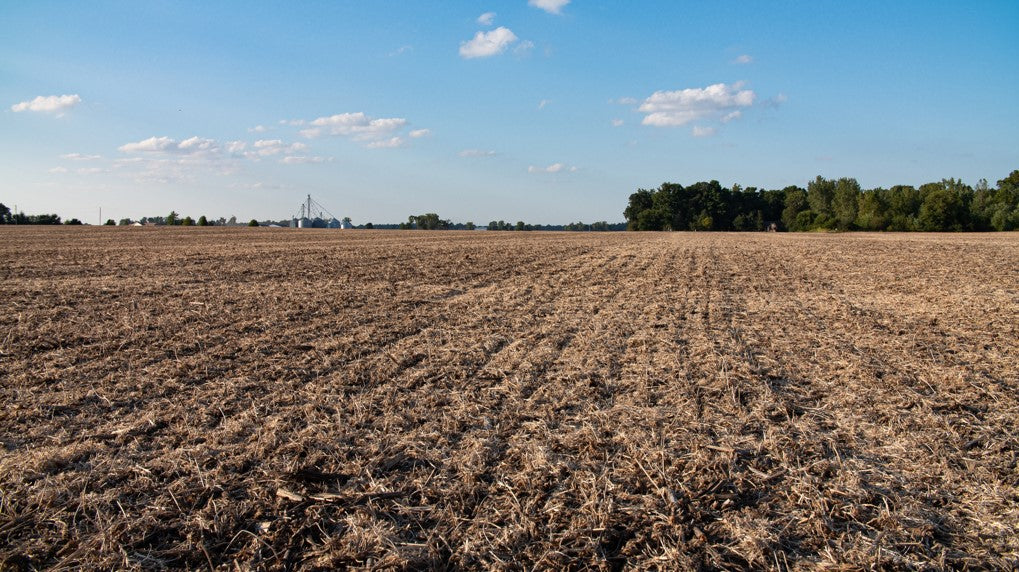
Help growers adopt regenerative farming practices, which have been shown to boost their profitability and be more beneficial for the planet.
For $80, you can help draw down 1 metric ton of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and compensate farmers for this societal benefit. Every ton counts!
For purchases of <500 credits:
- Credits will be retired in the public registry platform as a batch retirement on behalf of all small volume purchasers.
- Batch credit retirement will occur following each credit issuance
- No public attribution to individual buyers
- No guarantees of a specific vintage (vintages will never be older than 2018 and will be more recent with each batch)
For purchases of 500 - 5,000 credits:
- Orders will be reviewed by Indigo prior to execution of the transaction.
- Unique retirement in the public registry platform. We will reach out by email to confirm the retirement details.
- Anonymous retirement upon request
- Assignment of unique serial numbers
- Large volume credit retirements will begin in March, 2025
NOTE: Contact us if you would like to procure >5,000 credits.
CAR1459 - Indigo Ag U.S. Project No 1
| Project Type: | Agricultural Soil Carbon |
| Credit Type: | Removals + GHG Abatement |
| Crediting Program: | Climate Action Reserve |
| Methodology | Soil Enrichment Protocol |
| Project ID: | CAR1459 |
| Location: | United States |
| Project Start Year: | 2018 |
Click here for project details.
Share